List of counties in Alabama
The U.S. state of Alabama has 67 counties. Each county serves as the local level of government within its borders. The land enclosed by the present state borders was joined to the United States of America gradually. Following the American Revolutionary War, West Florida was ceded to Spain by treaty while the remainder was organized primarily as the Mississippi Territory, and later the Alabama Territory.[1] The territorial assembly established some of the earliest county divisions that have survived to the present, including the earliest county formation, that of Washington County, created on June 4, 1800.[2] In 1814, the Treaty of Fort Jackson opened the territory to American settlers, which in turn led to a more rapid rate of county creation. Alabama was admitted to the Union as the 22nd state in 1819.[3] The Alabama state legislature formed additional counties from former Indian lands as the Indian Removal Act took effect and settlers populated different areas of Alabama.[4] In 1820, Alabama had 29 counties. By 1830 there were 36 and Native Americans still occupied large areas of land in northeast and far western Alabama. By 1840, 49 counties had been created; 52 by 1850; 65 by 1870; and the present 67 counties by 1903.[5] Houston County was the last county created in the state, on February 9, 1903.[2]
According to 2006 U. S. Census estimates, the average population of Alabama's 67 counties is 68,642, with Jefferson County as the most populous (656,700), and Greene County (9,374) the least. The average land area is 757 sq mi (1,962 km2). The largest county is Baldwin (1,596 sq mi, 4,134 km2) and the smallest is Etowah (535 sq mi, 1,386 km2).[6] The Constitution of Alabama requires that any new county in Alabama cover at least 600 square miles (1,600 km2) in area, effectively limiting the creation of new counties in the state.[7]
The Alabama Department of Revenue's Motor Vehicle Division issues standard automobile license plates that bear a one- or two-digit number identifying the county in which the vehicle is registered. This number is given in the fourth column in the table below. The first three prefixes are reserved for the state's historically most populous counties, and thereafter proceed alphabetically. Individual license plate numbers are assigned sequentially in each licensing office. The numbers are in the format XA1111A or XXA111A, depending on whether the prefix is one or two digits. Overflow registrations are accommodated by substituting a letter for one of the registration numbers, such that XXZ999Z is followed by XXA0A0A.[8]
The Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) code, used by the United States government to uniquely identify counties, is provided with each entry. The FIPS code links in the table point to U. S. Census "quick facts" pages for each county.
Contents |
Counties
| County |
FIPS code [9] |
County seat [2] |
License # [10] |
Created [2] |
Formed from [11] |
Etymology [5][12] |
Population [6] |
Area [6] |
Map |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autauga County | 001 | Prattville | 4 | 1818 | Montgomery County | The Autauga or Atagi people, Native Americans who were a sub-group of the Alibamu | 49,730 | 596 sq mi (1,544 km2) | 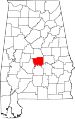 |
| Baldwin County | 003 | Bay Minette | 5 | 1809 | Washington County and West Florida | Abraham Baldwin (1754–1807), U.S. legislator from Georgia | 169,162 | 1,596 sq mi (4,134 km2) |
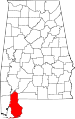 |
| Barbour County | 005 | Clayton | 6 | 1832 | Pike County | James Barbour (1775–1842), Governor of Virginia and U.S. Senator | 28,171 | 885 sq mi (2,292 km2) |
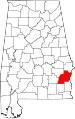 |
| Bibb County | 007 | Centreville | 7 | 1818 | Montgomery County (as Cahawba County) | William Wyatt Bibb (1781–1820), 1st Governor of Alabama | 21,482 | 623 sq mi (1,614 km2) |
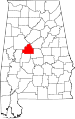 |
| Blount County | 009 | Oneonta | 8 | 1818 | Montgomery County and Indian territories | Willie Blount (1768–1835), Governor of Tennessee. | 56,436 | 646 sq mi (1,673 km2) |
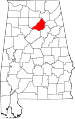 |
| Bullock County | 011 | Union Springs | 9 | 1866 | Barbour, Macon, Montgomery, and Pike Counties | Edward Bullock (1822–1861), colonel in the Confederate States Army | 10,906 | 625 sq mi (1,619 km2) |
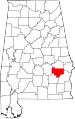 |
| Butler County | 013 | Greenville | 10 | 1819 | Conecuh and Monroe Counties | William Butler (?–1818), captain in Creek War | 20,520 | 777 sq mi (2,012 km2) |
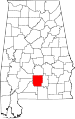 |
| Calhoun County | 015 | Anniston | 11 | 1832 | St. Clair County (as Benton County) | John C. Calhoun (1782–1850), 7th U.S. Vice President | 112,903 | 608 sq mi (1,575 km2) |
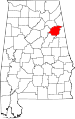 |
| Chambers County | 017 | LaFayette | 12 | 1832 | Montgomery County | Henry H. Chambers (1790–1826), U.S. Senator | 35,176 | 597 sq mi (1,546 km2) |
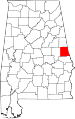 |
| Cherokee County | 019 | Centre | 13 | 1836 | Cherokee territory | Cherokee people | 24,863 | 553 sq mi (1,432 km2) |
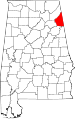 |
| Chilton County | 021 | Clanton | 14 | 1868 | Autauga, Bibb, Perry, and Shelby Counties (as Baker County) | William Parish Chilton (1810–1871), Alabama Supreme Court Justice and Confederate congressman | 41,953 | 694 sq mi (1,797 km2) |
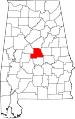 |
| Choctaw County | 023 | Butler | 15 | 1847 | Sumter and Washington Counties | Choctaw people, whose lands included Alabama | 14,656 | 914 sq mi (2,367 km2) |
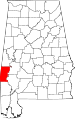 |
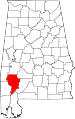
| Clarke County | 025 | Grove Hill | 16 | 1812 | Washington County | John Clarke (1766–1832), general from Georgia | 27,248 | 1,238 sq mi (3,206 km2) |
 |
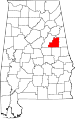
| Clay County | 027 | Ashland | 17 | 1866 | Randolph and Talladega Counties | Henry Clay (1777–1852), U.S. legislator from Kentucky | 13,829 | 605 sq mi (1,567 km2) |
 |
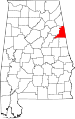
| Cleburne County | 029 | Heflin | 18 | 1866 | Calhoun, Randolph , and Talladega Counties | Patrick Cleburne (1828–1864), major general in Confederate States Army | 14,700 | 560 sq mi (1,450 km2) |
 |
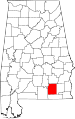
| Coffee County | 031 | Elba | 19 | 1841 | Dale County | John Coffee (1772–1833), military leader in War of 1812 and Creek War | 46,027 | 679 sq mi (1,759 km2) |
 |
| Colbert County | 033 | Tuscumbia | 20 | 1867 | Franklin County | George Colbert (?–1839) and Levi Colbert (?–1834), Chickasaw chiefs | 54,766 | 595 sq mi (1,541 km2) |
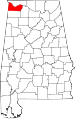 |
| Conecuh County | 035 | Evergreen | 21 | 1818 | Monroe County | The Conecuh River, which flows through the county | 13,403 | 851 sq mi (2,204 km2) |
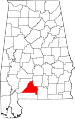 |
| Coosa County | 037 | Rockford | 22 | 1832 | Montgomery County | The Coosa River, which flows through the county, after a Native American village | 11,044 | 652 sq mi (1,689 km2) |
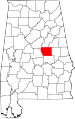 |
| Covington County | 039 | Andalusia | 23 | 1821 | Henry County | Leonard Covington (1768–1813), brigadier general in War of 1812 and U.S. Congressman | 37,234 | 1,034 sq mi (2,678 km2) |
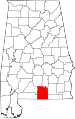 |
| Crenshaw County | 041 | Luverne | 24 | 1866 | Butler, Coffee, Covington, Lowndes, and Pike Counties | Anderson Crenshaw (1783–1847), settler of Butler County | 13,719 | 610 sq mi (1,580 km2) |
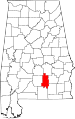 |
| Cullman County | 043 | Cullman | 25 | 1877 | Blount, Morgan, and Winston Counties | Colonel John G. Cullmann (1823–1895), founder of county seat | 80,187 | 738 sq mi (1,911 km2) |
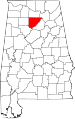 |
| Dale County | 045 | Ozark | 26 | 1824 | Covington and Henry Counties | Samuel Dale (1772–1841), brigadier general and state legislator | 48,392 | 561 sq mi (1,453 km2) |
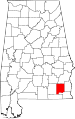 |
| Dallas County | 047 | Selma | 27 | 1818 | Monroe and Montgomery Counties | Alexander James Dallas (1759–1817) , U.S. Secretary of Treasury | 43,945 | 981 sq mi (2,541 km2) |
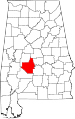 |
| DeKalb County | 049 | Fort Payne | 28 | 1836 | Cherokee territory | Johann de Kalb (1721–1780), major general in American Revolutionary War | 69,014 | 778 sq mi (2,015 km2) |
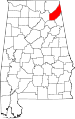 |
| Elmore County | 051 | Wetumpka | 29 | 1866 | Autauga, Coosa, Montgomery, and Tallapoosa Counties | John Archer Elmore (1762–1834), Revolutionary War veteran | 75,688 | 621 sq mi (1,608 km2) |
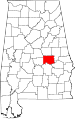 |
| Escambia County | 053 | Brewton | 30 | 1868 | Baldwin and Conecuh Counties | Escambia Creek, a tributary of the Conecuh River | 37,849 | 947 sq mi (2,453 km2) |
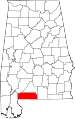 |
| Etowah County | 055 | Gadsden | 31 | 1866 | Blount, Calhoun, Cherokee, DeKalb, Marshall, and St. Clair Counties (as Baine County) | Etowah Indian Mounds | 103,362 | 535 sq mi (1,386 km2) |
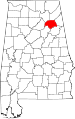 |
| Fayette County | 057 | Fayette | 32 | 1824 | Marion, Pickens, Tuscaloosa, and Walker Counties | Marquis de La Fayette (1757–1834), Revolutionary War commander | 18,005 | 628 sq mi (1,627 km2) |
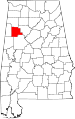 |
| Franklin County | 059 | Russellville | 33 | 1818 | Cherokee territory | Benjamin Franklin (1706–1790), politician, diplomat, inventor, and publisher | 30,847 | 636 sq mi (1,647 km2) |
 |
| Geneva County | 061 | Geneva | 34 | 1868 | Coffee, Dale, and Henry Counties | county seat, named after Geneva, New York | 25,868 | 576 sq mi (1,492 km2) |
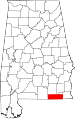 |
| Greene County | 063 | Eutaw | 35 | 1819 | Marengo and Tuscaloosa Counties | Nathanael Greene (1742–1786), Revolutionary War general | 9,374 | 646 sq mi (1,673 km2) |
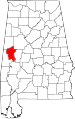 |
| Hale County | 065 | Greensboro | 36 | 1867 | Greene, Marengo, Perry, and Tuscaloosa Counties | Stephen F. Hale (1816–1862), lieutenant colonel in Confederate States Army | 18,236 | 644 sq mi (1,668 km2) |
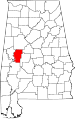 |
| Henry County | 067 | Abbeville | 37 | 1819 | Conecuh County | Patrick Henry (1736–1799), Revolutionary War patriot and Governor of Virginia | 16,706 | 562 sq mi (1,456 km2) |
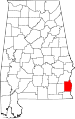 |
| Houston County | 069 | Dothan | 38 | 1903 | Dale, Geneva, and Henry Counties | George S. Houston (1811–1879), 24th Governor of Alabama and U.S. Congressman | 95,660 | 580 sq mi (1,502 km2) |
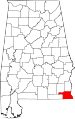 |
| Jackson County | 071 | Scottsboro | 39 | 1819 | Cherokee territory | Andrew Jackson (1767–1845), 7th U.S. President | 53,745 | 1,079 sq mi (2,795 km2) |
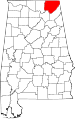 |
| Jefferson County | 073 | Birmingham | 1 | 1819 | Blount County | Thomas Jefferson (1743–1826), 3rd U.S. President | 656,700 | 1,113 sq mi (2,883 km2) |
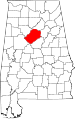 |
| Lamar County | 075 | Vernon | 40 | 1867 | Fayette and Marion Counties (as Jones County) | Lucius Q. C. Lamar (1825–1893), U.S. Supreme Court justice | 14,548 | 605 sq mi (1,567 km2) |
 |
| Lauderdale County | 077 | Florence | 41 | 1818 | Cherokee and Chickasaw territories | James Lauderdale (1780–1814), Colonel in War of 1812 | 87,891 | 669 sq mi (1,733 km2) |
 |
| Lawrence County | 079 | Moulton | 42 | 1818 | Cherokee territory | James Lawrence (1781–1813), naval officer in War of 1812 | 34,312 | 693 sq mi (1,795 km2) |
 |
| Lee County | 081 | Opelika | 43 | 1866 | Chambers, Macon, Russell, and Tallapoosa Counties | Robert E. Lee (1807–1870), Commander of the Confederate States Army | 125,781 | 609 sq mi (1,577 km2) |
 |
| Limestone County | 083 | Athens | 44 | 1818 | Elk and Madison Counties | Limestone Creek, named for local geological deposits | 72,446 | 568 sq mi (1,471 km2) |
 |
| Lowndes County | 085 | Hayneville | 45 | 1830 | Butler, Dallas, and Montgomery Counties | William Lowndes (1782–1822), U.S. Congressman from South Carolina | 12,759 | 718 sq mi (1,860 km2) |
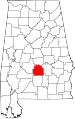 |
| Macon County | 087 | Tuskegee | 46 | 1832 | Montgomery County | Nathaniel Macon (1758–1837), U.S. legislator from North Carolina | 22,594 | 611 sq mi (1,582 km2) |
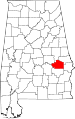 |
| Madison County | 089 | Huntsville | 47 | 1808 | Cherokee and Chickasaw territories | James Madison (1751–1836), 4th U.S. President | 304,307 | 805 sq mi (2,085 km2) |
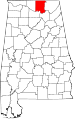 |
| Marengo County | 091 | Linden | 48 | 1818 | Choctaw territory | Battle of Marengo | 21,842 | 977 sq mi (2,530 km2) |
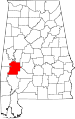 |
| Marion County | 093 | Hamilton | 49 | 1818 | Tuscaloosa County | Francis Marion (1732–1795), military leader in American Revolutionary War | 30,165 | 741 sq mi (1,919 km2) |
 |
| Marshall County | 095 | Guntersville | 50 | 1836 | Blount and Jackson Counties and Cherokee territory | John Marshall (1755–1832), Chief Justice of the United States 1801–1835 | 87,185 | 567 sq mi (1,469 km2) |
 |
| Mobile County | 097 | Mobile | 2 | 1812 | Mobile District of West Florida after annexation into Mississippi Territory | County seat and Mobile Bay, on which it is located, after the Maubila tribe of Native Americans | 404,157 | 1,233 sq mi (3,193 km2) |
 |
| Monroe County | 099 | Monroeville | 51 | 1815 | Creek territory | James Monroe (1758–1831), 5th U.S. President | 23,342 | 1,026 sq mi (2,657 km2) |
 |
| Montgomery County | 101 | Montgomery | 3 | 1816 | Monroe County | Lemuel P. Montgomery (?–1814), Major in Creek War | 223,571 | 790 sq mi (2,046 km2) |
 |
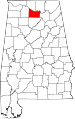
| Morgan County | 103 | Decatur | 52 | 1818 | Cherokee territory (as Cotaco County) | Daniel Morgan (1736–1802), U.S. Congressman | 115,237 | 582 sq mi (1,507 km2) |
 |
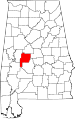
| Perry County | 105 | Marion | 53 | 1819 | Cahawba, Dallas, Marengo, and Tuscaloosa Counties | Oliver Hazard Perry (1795–1819), naval officer in War of 1812 | 11,186 | 719 sq mi (1,862 km2) |
 |
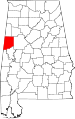
| Pickens County | 107 | Carrollton | 54 | 1820 | Tuscaloosa County | Andrew Pickens (1739–1817), General in the Revolutionary War | 20,133 | 881 sq mi (2,282 km2) |
 |
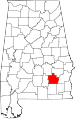
| Pike County | 109 | Troy | 55 | 1821 | Henry and Montgomery Counties | Zebulon Pike (1779–1813), explorer and officer in War of 1812 | 29,620 | 671 sq mi (1,738 km2) |
 |
| Randolph County | 111 | Wedowee | 56 | 1832 | St. Clair and Shelby Counties | John Randolph (1773–1833), U.S. Senator from Virginia | 22,673 | 581 sq mi (1,505 km2) |
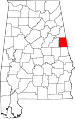 |
| Russell County | 113 | Phenix City | 57 | 1832 | Montgomery and Pike Counties | Gilbert C. Russell (1782-1861), officer in Creek War | 50,085 | 641 sq mi (1,660 km2) |
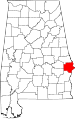 |
| St. Clair County | 115 | Ashville and Pell City | 59 | 1818 | Shelby County | Arthur St. Clair (1736–1818), President of Continental Congress | 75,232 | 634 sq mi (1,642 km2) |
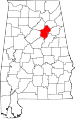 |
| Shelby County | 117 | Columbiana | 58 | 1818 | Montgomery County | Isaac Shelby (1750–1826), Governor of Kentucky | 178,182 | 795 sq mi (2,059 km2) |
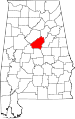 |
| Sumter County | 119 | Livingston | 60 | 1832 | Choctaw territory | Thomas Sumter (1734–1832), U.S. legislator | 13,606 | 905 sq mi (2,344 km2) |
 |
| Talladega County | 121 | Talladega | 61 | 1832 | St. Clair and Shelby Counties | Talatigi, Creek Indian name for the county seat, meaning "border town" | 80,271 | 740 sq mi (1,917 km2) |
 |
| Tallapoosa County | 123 | Dadeville | 62 | 1832 | Montgomery and Shelby Counties | Tallapoosa River | 41,010 | 718 sq mi (1,860 km2) |
 |
| Tuscaloosa County | 125 | Tuscaloosa | 63 | 1818 | Montgomery County and Choctaw territory | Tuscaloosa River and county seat | 171,159 | 1,324 sq mi (3,429 km2) |
 |
| Walker County | 127 | Jasper | 64 | 1823 | Blount, Jefferson, and Tuscaloosa Counties | John Williams Walker (1783–1823), U.S. Senator from Alabama | 70,034 | 794 sq mi (2,056 km2) |
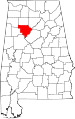 |
| Washington County | 129 | Chatom | 65 | 1800 | Adams and Pickering Counties of Mississippi Territory | George Washington (1732–1799), 1st U.S. President | 17,651 | 1,081 sq mi (2,800 km2) |
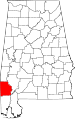 |
| Wilcox County | 131 | Camden | 66 | 1819 | Dallas and Monroe Counties | Joseph M. Wilcox (1790–1814), lieutenant in Creek War | 12,911 | 889 sq mi (2,302 km2) |
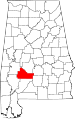 |
| Winston County | 133 | Double Springs | 67 | 1850 | Walker County (as Hancock County) | John A. Winston (1812–1871), 15th Governor of Alabama | 24,634 | 614 sq mi (1,590 km2) |
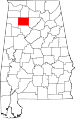 |
Former county names
| County[5] | Named for[5] | Changed to[2] |
|---|---|---|
| Baine County | David W. Baine, Colonel in the Civil War | Etowah County in 1868 |
| Baker County | Alfred Baker, a local landowner | Chilton County in 1874 |
| Benton County | Thomas Hart Benton, U. S. Senator from Missouri | Calhoun County in 1858, honoring Benton's rival John C. Calhoun of South Carolina after Benton's renunciation of slavery |
| Cahawba County | former state capitol of Cahawba | Bibb County in 1820 |
| Cotaco County | Cotaco Creek, a tributary of the Tennessee River | Morgan County in 1821 |
| Elk County | Elk River | Lauderdale County and Limestone County in 1818 |
| Hancock County | John Hancock, signer of the Declaration of Independence | Winston County in 1858 |
| Jones County | Josiah Jones, a local political leader | Covington County in 1868 after Jones refused the honor |
| Jones County | E.P. Jones, a local landowner | Sanford County, which subsequently became Lamar County in 1877 |
| Sanford County | H.C. Sanford, a local landowner | Lamar County in 1877 |
References
- General
- "CountyState.info Alabama". Official County Websites. http://www.countystate.info/alabama.htm. Retrieved 2007-09-13.
- Specific
- ↑ "Alabama History Timeline, 1701-1800". Alabama Department of Archives and History. http://www.archives.state.al.us/timeline/al1702.html. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 National Association of Counties. "NACo - Find a county". http://www.naco.org/Template.cfm?Section=Find_a_County&Template=/cffiles/counties/state.cfm&state.cfm&statecode=AL. Retrieved 2008-04-30.
- ↑ "Alabama History Timeline, 1801-1860". Alabama Department of Archives and History. http://www.archives.state.al.us/timeline/al1801.html. Retrieved 2009-05-18.
- ↑ "Alabama Counties: Cherokee". Alabama Department of Archives and History. http://www.archives.state.al.us/counties/cherokee.html. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Foscue, Virginia O. (1989) Place Names in Alabama. Tuscaloosa, Alabama: University of Alabama Press. ISBN 081730410X
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 "Alabama QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". State & County QuickFacts. http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/maps/alabama_map.html. Retrieved 2009-05-25.
- ↑ "Alabama Constitution of 1901". Wikisource, The Free Library. http://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Alabama_State_Constitution_of_1901/Initial_Constitution#Section_39. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
- ↑ Nicholson, David. "Alabama License Plates, 1969-present". License Plates of North America, 1969–present. http://www.15q.net/al.html. Retrieved 2007-08-08.
- ↑ "EPA County FIPS Code Listing". EPA.gov. http://www.epa.gov/enviro/html/codes/al.html. Retrieved 2008-02-23.
- ↑ Nicholson, David. "Alabama County Codes". License Plates of North America, 1969–present. http://www.15q.net/alco.html. Retrieved 2009-05-25.
- ↑ Owen, Thomas McAdory; Owen, Marie Bankhead (1921). History of Alabama and Dictionary of Alabama Biography. Chicago: S.J. Clarke Publishing Company.
- ↑ "Alabama Counties". Alabama Department of Archives and History. http://www.archives.state.al.us/counties.html. Retrieved 2009-06-01.
See also
- List of census county divisions in Alabama
External links
- Map series showing evolution of county boundaries. Cartographic Research Laboratory. University of Alabama Department of Geography.
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||